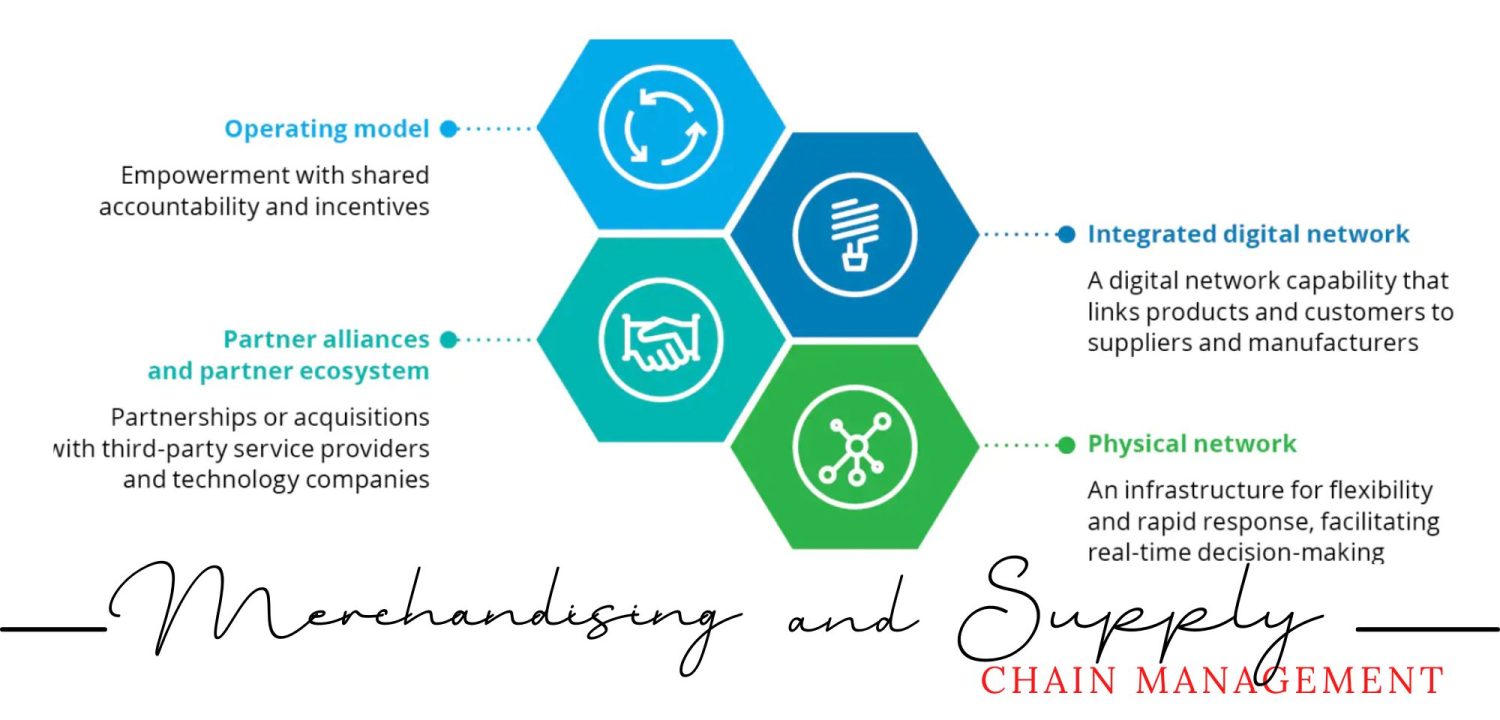
Merchandising and Supply Chain Management
Merchandising and supply chain management are two important components of successful retail operations. While merchandising focuses on selecting and displaying products to maximize sales and profits, supply chain management focuses on the movement of goods and materials from suppliers to manufacturers to retailers and ultimately to consumers. Here’s how these two areas work together:
- Product selection: Merchandisers work closely with supply chain managers to select products that meet customer demand while also considering supply chain logistics. Supply chain managers provide information on the availability, cost, and lead times of products, which helps merchandisers make informed decisions about what products to stock.
- Supplier selection: Supply chain managers are responsible for selecting and managing suppliers, negotiating contracts, and ensuring the timely delivery of goods. Merchandisers may be involved in supplier selection, providing input on product quality and availability.
- Inventory management: Effective supply chain management is crucial for inventory management. Supply chain managers must forecast demand, manage inventory levels, and ensure that products are delivered on time. Merchandisers use this information to plan promotions, sales, and product displays.
- Logistics: Supply chain managers are responsible for the logistics of moving products from suppliers to retailers. This includes transportation, warehousing, and distribution. Merchandisers work with supply chain managers to plan the most effective logistics strategy, such as deciding when to order products and how to allocate them to different stores.
- Customer satisfaction: Both merchandising and supply chain management play a crucial role in ensuring customer satisfaction. Effective merchandising can lead to increased sales and customer loyalty, while efficient supply chain management ensures that products are available when and where customers want them.
Merchandising and supply chain management are closely linked and must work together to ensure that retail operations are successful. By collaborating and sharing information, merchandisers and supply chain managers can optimize inventory levels, improve logistics, and ultimately increase customer satisfaction and profits.
What is Merchandise Management?
Merchandise management is the process of planning, coordinating, and controlling the selection, pricing, and presentation of products in order to maximize sales and profitability. This involves a range of activities, including product selection, procurement, inventory management, pricing, promotions, and visual merchandising.
The primary goal of merchandise management is to ensure that the right products are available in the right quantities, at the right time and place, and at the right price. This requires a deep understanding of customer needs and preferences, as well as the ability to effectively manage the supply chain and inventory levels.
Effective merchandise management involves a range of best practices and techniques, such as:
- Product selection: Retailers must carefully choose which products to offer based on factors such as customer demand, market trends, and competitive offerings. This involves conducting market research, analyzing sales data, and staying up-to-date on industry trends.
- Procurement: Retailers must work with suppliers to negotiate pricing, delivery schedules, and quality standards. This requires strong communication skills, a solid understanding of supply chain management, and the ability to build strong supplier relationships.
- Inventory management: Retailers must maintain optimal inventory levels to ensure that they have enough stock to meet customer demand without tying up too much capital in excess inventory. This involves forecasting demand, monitoring inventory levels, and implementing effective replenishment strategies.
- Pricing and promotions: Retailers must set prices that are competitive and attractive to customers, while also ensuring that they generate a profit. This involves analyzing market trends, understanding customer behavior, and designing effective promotional campaigns.
- Visual merchandising: Retailers must present products in an attractive and compelling manner to encourage customers to make a purchase. This involves designing effective store layouts, creating eye-catching displays, and using lighting and other visual elements to create a welcoming atmosphere.
By effectively managing merchandise, retailers can improve sales and profitability, build customer loyalty, and create a strong brand identity.
What is Merchandising?
Merchandising refers to the process of selecting, procuring, presenting, and selling products to customers with the aim of generating maximum sales and profitability. It involves a range of activities, including product selection, inventory management, pricing, promotions, and visual merchandising.
The goal of merchandising is to ensure that the right products are available to customers at the right time and place, and at the right price. This requires a deep understanding of customer needs and preferences, as well as the ability to effectively manage the supply chain and inventory levels.
Merchandising involves a range of best practices and techniques, such as:
- Product selection: Retailers must choose which products to offer based on factors such as customer demand, market trends, and competitive offerings. This involves conducting market research, analyzing sales data, and staying up-to-date on industry trends.
- Procurement: Retailers must work with suppliers to negotiate pricing, delivery schedules, and quality standards. This requires strong communication skills, a solid understanding of supply chain management, and the ability to build strong supplier relationships.
- Inventory management: Retailers must maintain optimal inventory levels to ensure that they have enough stock to meet customer demand without tying up too much capital in excess inventory. This involves forecasting demand, monitoring inventory levels, and implementing effective replenishment strategies.
- Pricing and promotions: Retailers must set prices that are competitive and attractive to customers, while also ensuring that they generate a profit. This involves analyzing market trends, understanding customer behavior, and designing effective promotional campaigns.
- Visual merchandising: Retailers must present products in an attractive and compelling manner to encourage customers to make a purchase. This involves designing effective store layouts, creating eye-catching displays, and using lighting and other visual elements to create a welcoming atmosphere.
Effectively merchandising products, retailers can improve sales and profitability, build customer loyalty, and create a strong brand identity.
What is Supply Chain Management?
Supply chain management (SCM) is the process of planning, implementing, and controlling the operations of a supply chain. It involves coordinating the flow of goods and services from raw materials to finished products, and from suppliers to customers, in the most efficient and cost-effective manner possible.
The goal of SCM is to optimize the entire supply chain, from procurement of raw materials to delivery of finished products to customers, while minimizing costs and maximizing customer satisfaction. To achieve this, SCM requires collaboration and communication among suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, retailers, and customers.
SCM encompasses a wide range of activities, including:
- Planning: This involves developing a strategy for the supply chain, setting goals and objectives, and creating a plan for how to achieve them.
- Sourcing: This involves selecting and managing suppliers, negotiating contracts, and ensuring that raw materials and components are of high quality and delivered on time.
- Production: This involves managing the production process, including scheduling, inventory management, and quality control.
- Logistics: This involves managing the movement of goods from suppliers to manufacturers to retailers and ultimately to customers, including transportation, warehousing, and distribution.
- Customer service: This involves managing relationships with customers, ensuring that products are delivered on time and in good condition, and addressing any issues or concerns they may have.
SCM is critical to the success of any business that relies on a complex network of suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers to deliver products to customers. By optimizing the supply chain, businesses can reduce costs, improve efficiency, and increase customer satisfaction, ultimately leading to increased profits and competitive advantage.
How do Merchandising and Supply Chain Management Work Together?
Merchandising and supply chain management are two key aspects of retail operations that work closely together to ensure the success of a business. Merchandising focuses on the selection, pricing, and presentation of products, while supply chain management is responsible for ensuring the efficient flow of goods and services from suppliers to customers. In this article, we will explore how merchandising and supply chain management work together to maximize profits and customer satisfaction.
Effective Merchandising and Supply Chain Management
Merchandising and supply chain management are interconnected and interdependent. An effective merchandising strategy requires a reliable supply chain that can deliver products to the store or warehouse in a timely and cost-effective manner. Similarly, an efficient supply chain is crucial for ensuring that the right products are available at the right time and place to meet customer demand.
Merchandising and supply chain management work together in several key ways:
- Product selection and procurement: Merchandisers are responsible for selecting and sourcing products that will appeal to customers and meet their needs. Supply chain managers work closely with merchandisers to identify suppliers, negotiate contracts, and ensure that products are delivered on time and in good condition.
- Inventory management: Both merchandisers and supply chain managers are involved in managing inventory levels to ensure that the right products are available when customers need them. Merchandisers are responsible for forecasting demand, while supply chain managers ensure that inventory levels are sufficient to meet that demand without overstocking and tying up valuable capital.
- Pricing and promotions: Merchandisers set prices and promotions based on customer demand and market conditions. Supply chain managers work with merchandisers to identify the most cost-effective sourcing and distribution strategies that allow for competitive pricing and profitable promotions.
- Logistics and distribution: Supply chain managers are responsible for managing the logistics and distribution of products from suppliers to stores or warehouses, while merchandisers ensure that products are presented in an attractive and compelling manner to maximize sales.
The Benefits of Effective Merchandising and Supply Chain Management
Effective merchandising and supply chain management can provide several benefits to retailers, including:
- Increased sales: By ensuring that the right products are available at the right time and place, retailers can increase sales and customer satisfaction.
- Improved inventory management: Effective merchandising and supply chain management can reduce inventory holding costs and minimize the risk of overstocking or stockouts.
- Enhanced customer experience: By providing high-quality products and services, retailers can build customer loyalty and increase customer satisfaction.
- Increased profitability: Effective merchandising and supply chain management can help retailers reduce costs, increase margins, and improve overall profitability.
In conclusion, merchandising and supply chain management are two critical components of retail operations that work closely together to ensure the success of a business. By working collaboratively and leveraging each other’s strengths, retailers can optimize their supply chain and maximize profits and customer satisfaction.