What is Merchandise Inventory on a Balance Sheet
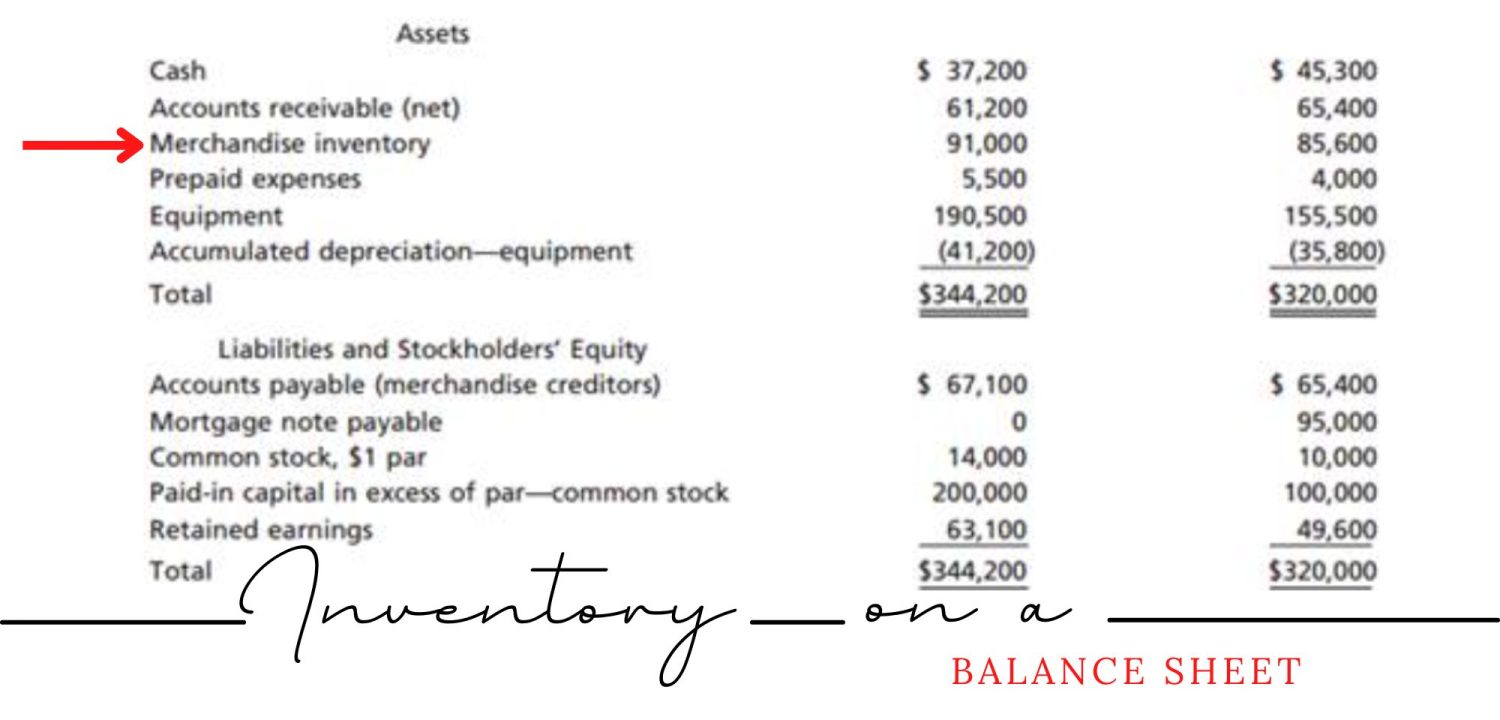
Merchandise inventory is a term used to describe the value of a company’s unsold goods or products that are held for sale to customers. It is considered a current asset on a balance sheet because it is expected to be sold within a year. In this article, we will discuss what merchandise inventory is on a balance sheet and its importance to a company’s financial health.
Merchandise inventory is a key component of a company’s balance sheet, which provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It is reported under the “Current Assets” section, which also includes items such as cash, accounts receivable, and prepaid expenses.
The value of merchandise inventory is reported at its cost, which includes the purchase price plus any additional costs incurred to bring the goods to their current location and condition, such as shipping, handling, and storage fees. Merchandise inventory is typically reported on the balance sheet using the “lower of cost or market” (LCM) method, which means that it is valued at the lower of its cost or its market value.
The LCM method is used to prevent companies from overstating the value of their inventory on the balance sheet. If the market value of the inventory falls below its cost, the company must write down the value of the inventory to its market value, which reduces the value of the inventory on the balance sheet and lowers the company’s net income.
Merchandise inventory is important on a balance sheet because it is a significant asset for many companies, particularly those in the retail and manufacturing industries. The amount of inventory a company holds can have a significant impact on its profitability and cash flow. If a company holds too much inventory, it can tie up cash and lead to increased storage costs, while holding too little inventory can result in lost sales and reduced customer satisfaction.
In addition, the value of merchandise inventory can provide insights into a company’s financial health and performance. By tracking changes in the value of merchandise inventory over time, investors and analysts can evaluate a company’s ability to manage its inventory effectively and make informed decisions about the company’s financial prospects.
Merchandise inventory is an important current asset that is reported on a company’s balance sheet. It represents the value of a company’s unsold goods and products that are held for sale to customers. The value of merchandise inventory is reported at its cost using the lower of cost or market method and is an important indicator of a company’s financial health and performance.
How to Read a Balance Sheet
A balance sheet is an important financial statement that provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It lists a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity, and provides important insights into the financial health of the company. In this article, we will discuss how to read a balance sheet and interpret the information it provides.
- Understanding the Structure of a Balance Sheet
A balance sheet is structured in three main sections: assets, liabilities, and equity. Assets are listed first and are followed by liabilities and equity. Assets are what a company owns, liabilities are what it owes, and equity is what’s left over after liabilities are subtracted from assets.
- Analyzing Assets
Assets are typically listed in order of liquidity, which is the ease with which they can be converted into cash. The most liquid assets are listed first, followed by less liquid assets. Common types of assets include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and property, plant, and equipment (PP&E). It’s important to analyze the composition of a company’s assets to gain insights into its financial health and performance.
- Analyzing Liabilities
Liabilities are listed in order of maturity, which is the time frame in which they are due. Current liabilities, which are due within one year, are listed first, followed by long-term liabilities. Common types of liabilities include accounts payable, loans, and bonds. It’s important to analyze the composition of a company’s liabilities to understand its debt load and the risk associated with its debt.
- Analyzing Equity
Equity represents the residual interest in the assets of the company after all liabilities are paid. It includes common stock, retained earnings, and other comprehensive income. It’s important to analyze a company’s equity to understand the value of the company and the amount of money that has been invested in the company.
- Analyzing Ratios
Ratios can be calculated using information from the balance sheet to gain insights into a company’s financial health and performance. Common ratios include the current ratio, which measures a company’s ability to pay its short-term obligations, and the debt-to-equity ratio, which measures a company’s debt load relative to its equity.
Therefore, reading a balance sheet is critical for investors, analysts, and business owners to gain insights into a company’s financial health and performance. By analyzing the composition of a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity, and calculating ratios, it’s possible to gain a comprehensive understanding of a company’s financial position and make informed decisions about investing, lending, and managing the company.
Why is Merchandise Important on a Balance Sheet
Merchandise inventory is an essential component of a company’s balance sheet. It represents the value of the goods that a company holds for sale to customers, and is classified as a current asset because it is expected to be converted into cash within one year. In this article, we will discuss why merchandise is important on a balance sheet.
- Importance of Inventory Management
Merchandise inventory represents a significant investment for many companies, particularly those in the retail and manufacturing industries. Effective inventory management is critical for ensuring that a company has the right amount of inventory on hand to meet customer demand, while avoiding excess inventory that ties up capital and can lead to obsolescence or spoilage.
- Impact on Financial Statements
Merchandise inventory is an important component of a company’s financial statements, particularly the balance sheet. It is reported at the lower of cost or market value, meaning that it is valued at the amount that a company paid for it or its current market value, whichever is lower. This ensures that inventory is not overvalued on the balance sheet, which could lead to overstating a company’s assets.
- Impact on Profitability
Merchandise inventory has a direct impact on a company’s profitability. When inventory is sold, it generates revenue and contributes to gross profit. However, if inventory is not managed effectively and becomes obsolete or spoils, it can result in significant write-offs that can negatively impact profitability.
- Impact on Cash Flow
Merchandise inventory also has an impact on a company’s cash flow. When inventory is purchased, it represents a cash outflow, while the sale of inventory represents a cash inflow. Effective inventory management is critical for ensuring that a company has enough inventory to meet customer demand, while avoiding excess inventory that ties up cash.
Merchandise inventory is an important component of a company’s balance sheet. It represents a significant investment for many companies and has a direct impact on profitability and cash flow. Effective inventory management is critical for ensuring that a company has the right amount of inventory on hand to meet customer demand, while avoiding excess inventory that can negatively impact financial performance.
What is the Benefit of Knowing How to Read Your Balance Sheet
A balance sheet is a financial statement that shows a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It provides a snapshot of the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity. Knowing how to read a balance sheet is essential for business owners, investors, and financial analysts because it helps them understand a company’s financial health and performance. In this article, we will discuss the benefits of knowing how to read your balance sheet.
- Assessing financial health: A balance sheet provides a clear picture of a company’s financial health by showing its assets, liabilities, and equity. By analyzing these elements, investors can determine whether the company has enough resources to meet its obligations and generate profits. For example, if a company has more assets than liabilities, it indicates that the company is in good financial health.
- Analyzing liquidity: Liquidity refers to a company’s ability to meet its short-term financial obligations. A balance sheet can help investors and business owners analyze a company’s liquidity by providing information about its current assets and liabilities. If a company has more current assets than current liabilities, it indicates that the company has sufficient resources to meet its short-term obligations.
- Identifying trends: By comparing balance sheets over time, investors and financial analysts can identify trends in a company’s financial performance. For example, if a company’s inventory has been steadily increasing over time, it may indicate that the company is experiencing growth.
- Identifying risks: A balance sheet can also help identify risks associated with a company’s financial position. For example, if a company has a high debt-to-equity ratio, it may indicate that the company has a high level of debt and may have difficulty meeting its obligations in the future.
- Making informed decisions: By understanding a company’s financial health and performance, investors and business owners can make informed decisions about investing in the company or managing the business. For example, if a company has a strong balance sheet, it may be a good investment opportunity, while a weak balance sheet may indicate that the company is a higher risk.
Knowing how to read your balance sheet is essential for understanding a company’s financial health and performance. It provides critical information about a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity, which can help investors and business owners make informed decisions about investing in the company or managing the business. By analyzing the information provided by a balance sheet, investors and business owners can identify trends, assess liquidity, and identify risks associated with a company’s financial position.
Is Inventory a Current Asset?
Inventory is considered a current asset on a company’s balance sheet. A current asset is an asset that can be easily converted into cash or is expected to be used within one year or less. Inventory meets these criteria because it is expected to be sold, used, or consumed within a year.
Inventory is defined as the goods that a company has on hand and intends to sell to its customers. This can include raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods. For retail businesses, inventory typically consists of products purchased from suppliers and intended for resale to customers. For manufacturing businesses, inventory can include raw materials, components, and finished goods.
The value of inventory on a company’s balance sheet represents the cost of the goods that have not yet been sold. The cost of inventory includes the purchase price of the goods, as well as any direct costs associated with acquiring, producing, or preparing the goods for sale, such as shipping and handling costs or labor costs.
The value of inventory can have a significant impact on a company’s financial statements, particularly its income statement and balance sheet. If the value of inventory is overstated, it can lead to an overstatement of a company’s assets, which can inflate the company’s profitability and financial health. On the other hand, if the value of inventory is understated, it can lead to an understatement of a company’s assets, which can reduce the company’s profitability and financial health.
In conclusion, inventory is considered a current asset because it is expected to be sold, used, or consumed within one year or less. The value of inventory on a company’s balance sheet represents the cost of the goods that have not yet been sold, and it can have a significant impact on a company’s financial statements. It is important for businesses to accurately value their inventory to ensure that their financial statements are accurate and reliable.